(LifeSiteNews) — A newly published secular study found that Vatican II “triggered a decline” in worldwide Catholic Mass attendance relative to religious service attendance of other religions, including Protestant Christianity.
By examining the religious service attendance rates for 66 countries as far back as 1920, the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) found that “compared to other countries, Catholic countries experienced a steady decline in the monthly adult religious service attendance rate starting immediately after Vatican II” in 1965, the final year of the council.
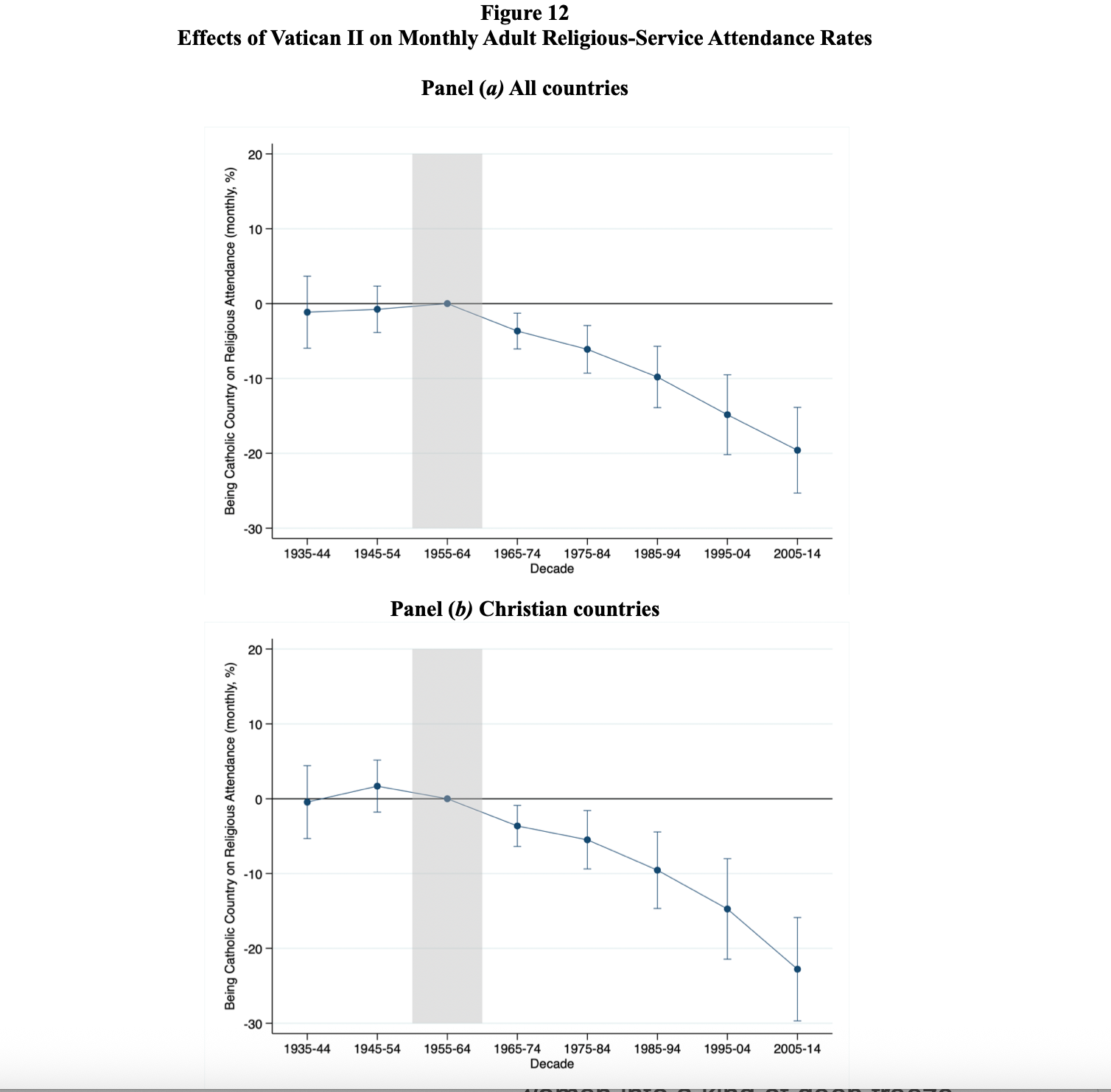
Catholic countries were defined as those with a Catholic population of 50% or greater and included nations such as Ireland, Italy, Austria, France, Brazil, the Philippines, and Mexico.
A graph representing the researchers’ data shows that monthly religious service attendance in Catholic countries decreased by at least 20 percentage points relative to that of all other countries as well as relative to “Christian” countries, with a significant decline seen first in the period from 1965 to 1974. Mass attendance in Catholic countries fell on average by four percentage points per decade from 1965 to 2015.
These findings accord with those of French historian Guillaume Cuchet, who in 2022 published an analysis that found 1965, the year the Second Vatican Council ended, marked the beginning of the “collapse” of the practice of Catholicism in France.
As Phil Lawler has noted, the findings of NBER regarding Vatican II’s effects on Mass attendance are noteworthy because NBER is a “heavyweight” economic research institution with “no dog in the fight” of Catholicism’s internal debates.
While NBER has not investigated what it was specifically about Vatican II that precipitated the steep worldwide drop in Mass attendance, its researchers have cited several potential factors proposed by author Andrew Greeley, including changes to the Mass itself, a new ecumenical outlook on other religions, and the abolishing the requirement of certain practices such as abstinence from meat on Fridays.
Significant changes to the Mass itself began with the implementation of The First Instruction on the Proper Implementation of the Constitution of the Sacred Liturgy, Inter oecumenici, on March 7, 1965. While it aimed to make the Mass more “accessible” and palatable, its changes would have come across as foreign and even as a shock to a number of Catholics for whom the Mass had remained virtually unchanged their entire life.
For example, Inter oecumenici stipulated that “the main altar should preferably be freestanding, to permit walking around it and celebration facing the people.” This itself is a radical change, since it imposed a literal 180-degree reversal of the very orientation of the Mass.
Already in 1965, Psalm 42 at the beginning of the Mass, and the Last Gospel and Leonine prayers at the end were suppressed; the congregation was to recite the Our Father together with the priest; the lessons, epistle, and gospel were to be read or sung facing the people; in non-solemn Masses, laypeople were to “read the lessons and epistles with the intervening chants” as the priest sat and listened; Mass-goers were to say “Amen” before receiving Holy Communion.
As the French historian Cuchet noted in reference to declining Mass attendance, while these changes in ritual may seem “secondary to intellectuals,” they “are actually psychological and anthropological determinants.”
While liturgical changes would have been the most vivid and palpable of Vatican II’s effects for most Mass-going Catholics, researchers have argued that Vatican II’s apparent doctrinal shift should not be discounted.
“The explicit questioning of centuries-old doctrines, such as the forbidding of birth control, may have shattered the perception of an immovable, truth-holding Church and replaced it with a model whereby individuals had a more direct relationship with God and were, therefore, less dependent on the Church and its formal services,” noted the researchers, echoing Greeley.
While the Church went on to uphold its ban on contraception, it was leaked to the press in 1967 that a significant majority of the members of Pope Paul VI’s commission on birth control, including 60 of 64 theologians and nine of 15 cardinals, supported lifting the ban.
While the Catholic Church cannot change doctrine, Vatican II was unique in Church history for ambiguous statements that gave the widespread impression that the Church had changed its teaching. For example, Unitatis Redintegratio said it is sometimes permissible to hold common worship with non-Catholics, whereas at least three Church councils have explicitly prohibited praying in common with heretics.
For Catholics who may not have been keeping abreast of the changes of the Vatican II documents, the slew of changes in practice, such as the abandonment of certain devotional prayers and the “sudden silence” on the Four Last Things during sermons (Death, Judgment, Heaven and Hell) may have similarly given the impression that the Church had undergone a substantial change in teaching. As Dr. John Pepino put it, while summarizing the research of Cuchet, “An institution that admits to having been wrong yesterday may well be wrong today, too.”
















